Why Public Health Is Important
For Developing Countries
In
this article, we will delve into the crucial topic of why public health is of
paramount importance for developing countries. Public health plays a pivotal
role in the overall well-being and progress of a nation, especially in regions
where resources are limited, and populations are vulnerable. Developing
countries face unique challenges, and addressing public health concerns is not
only a humanitarian obligation but also a key factor in driving sustainable
development and prosperity.
The
Significance of Public Health in Developing Countries
1.
Enhancing Quality of Life
Public
health initiatives have a direct and positive impact on the quality of life of
citizens in developing countries. By promoting preventive measures, such as
vaccinations, sanitation, and nutrition programs, we can significantly reduce
the burden of infectious diseases and enhance overall life expectancy. This, in
turn, contributes to a more productive and economically stable society.
2.
Economic Growth and Productivity
A
healthy population is essential for a country's economic growth and
productivity. When individuals are plagued by preventable diseases, they are
unable to contribute fully to the workforce. By investing in public health
infrastructure, such as healthcare facilities, trained healthcare
professionals, and disease monitoring systems, developing countries can unlock
the full potential of their human capital and foster economic development.
3.
Reducing Healthcare Costs
Prevention
is more cost-effective than treatment, and this adage holds true in the realm
of public health. By focusing on preventive healthcare measures, such as health
education and early disease detection, we can reduce the financial burden on
healthcare systems in developing countries. This, in turn, frees up resources
to address other pressing needs and improve overall healthcare access.
4.
Improving Maternal and Child Health
Maternal
and child health is a critical aspect of public health in developing countries.
High-quality prenatal care, skilled attendance during childbirth, and postnatal
support significantly reduce maternal and infant mortality rates. Additionally,
proper nutrition and immunization programs safeguard the health of newborns and
ensure healthy childhood development.
5.
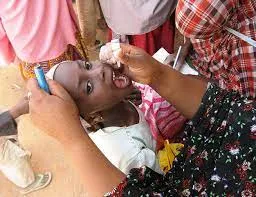
Combating Infectious Diseases
Developing
countries often grapple with infectious diseases, such as malaria,
tuberculosis, and HIV/AIDS. Robust public health measures, including disease
surveillance, prevention campaigns, and access to essential medications, are
instrumental in controlling the spread of these illnesses and preventing
widespread outbreaks.
Challenges
and Roadblocks
1. Limited Resources
One
of the most significant challenges faced by developing countries in improving
public health is the scarcity of resources. Insufficient funding, inadequate
infrastructure, and a shortage of trained healthcare professionals hinder the
implementation of comprehensive health programs.
2.
Cultural and Social Factors
Cultural
beliefs and social norms can impact the acceptance of public health
interventions. We must approach healthcare initiatives with sensitivity and
cultural awareness to foster trust and cooperation within the community.
3.
Political Will and Governance
Strong
political will and effective governance are crucial for successful public
health initiatives. We need government commitment to allocate resources,
develop policies, and implement programs that prioritize public health and
well-being.
Best
Practices in Public Health for Developing Countries
1.
Community Engagement and Education
Engaging
with local communities and promoting health education are foundational to
successful public health interventions. By empowering individuals with
knowledge about disease prevention, hygiene practices, and healthy lifestyles,
we can create a health-conscious society.
2.
Collaborative Partnerships
Public-private
partnerships and collaborations with non-governmental organizations (NGOs) play
a vital role in bolstering public health efforts in developing countries. These
partnerships bring together expertise, resources, and innovative solutions to
address healthcare challenges effectively.
3.
Leveraging Technology
Advancements
in technology can revolutionize public health in developing countries. Mobile
health applications, telemedicine, and health information systems can bridge
gaps in healthcare access, especially in remote areas.
4.
Strengthening Healthcare Infrastructure
Investments
in healthcare infrastructure, including the construction of hospitals, clinics,
and health centers, are indispensable for expanding healthcare coverage and
providing essential services to all citizens.
Conclusion
In
conclusion, the significance of public health in developing countries cannot be
overstated. It is not only a matter of improving individual health but also an
investment in a nation's prosperity and progress. By prioritizing public health
initiatives, developing countries can overcome numerous challenges and pave the
way for a healthier, more prosperous future.
for more:
Importance of a Public Health Degree in Developing Countries
Why is Public Health so important?

No comments
if you have any doubt, please comment